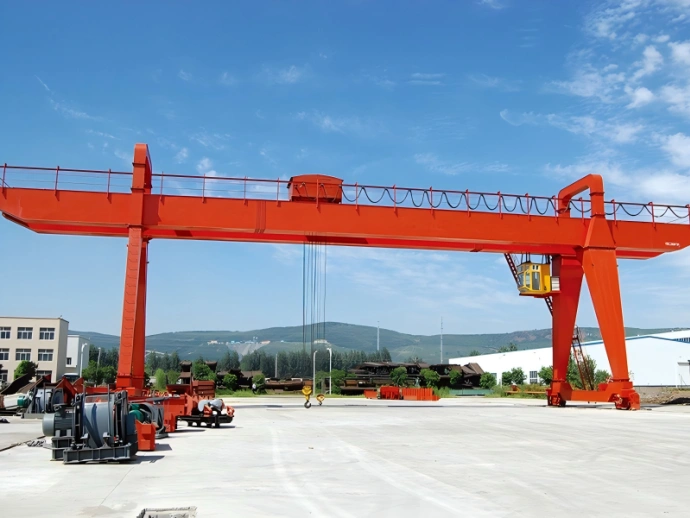
As highly efficient lifting equipment, double-girder gantry cranes play a crucial role in modern industrial and construction sectors. Their design offers several distinct advantages, which can be outlined and expanded upon as follows:
1. Robust Structure with Enhanced Load Capacity
The double-girder design—typically constructed with box or truss girders—provides greater rigidity and torsional resistance compared to single-girder systems. This configuration distributes loading stresses more effectively, significantly improving stability and enabling the handling of heavier loads, ranging from several tons to over a thousand tons. The ample clearance under the girders also allows for safe and unobstructed movement of large-scale items such as prefabricated components, heavy machinery, and shipping containers, making these cranes ideal for heavy industries, shipbuilding, and bridge construction.
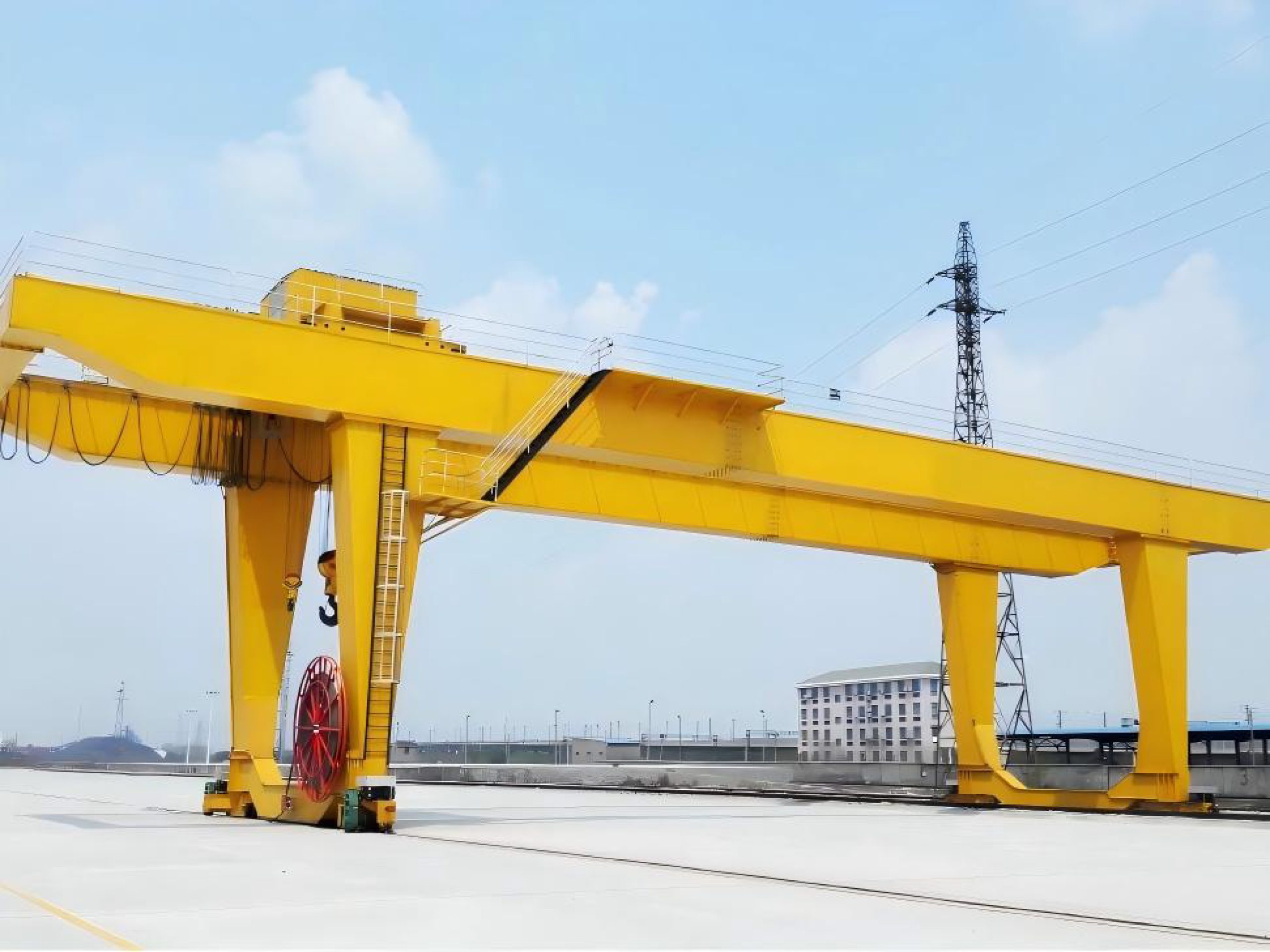

2. Wide Working Range and High Operational Efficiency
With spans that can extend from several meters to more than a hundred meters, double-girder gantry cranes cover extensive areas, making them well-suited for long-distance material handling in open spaces like storage yards, freight terminals, and ports. The use of twin hoists or main/auxiliary hook arrangements further enhances flexibility, enabling simultaneous multi-position operations and reducing transfer times. Moreover, the travel mechanism often incorporates dual-rail or multi-drive synchronization technology, ensuring smooth movement even under large spans and windy conditions.
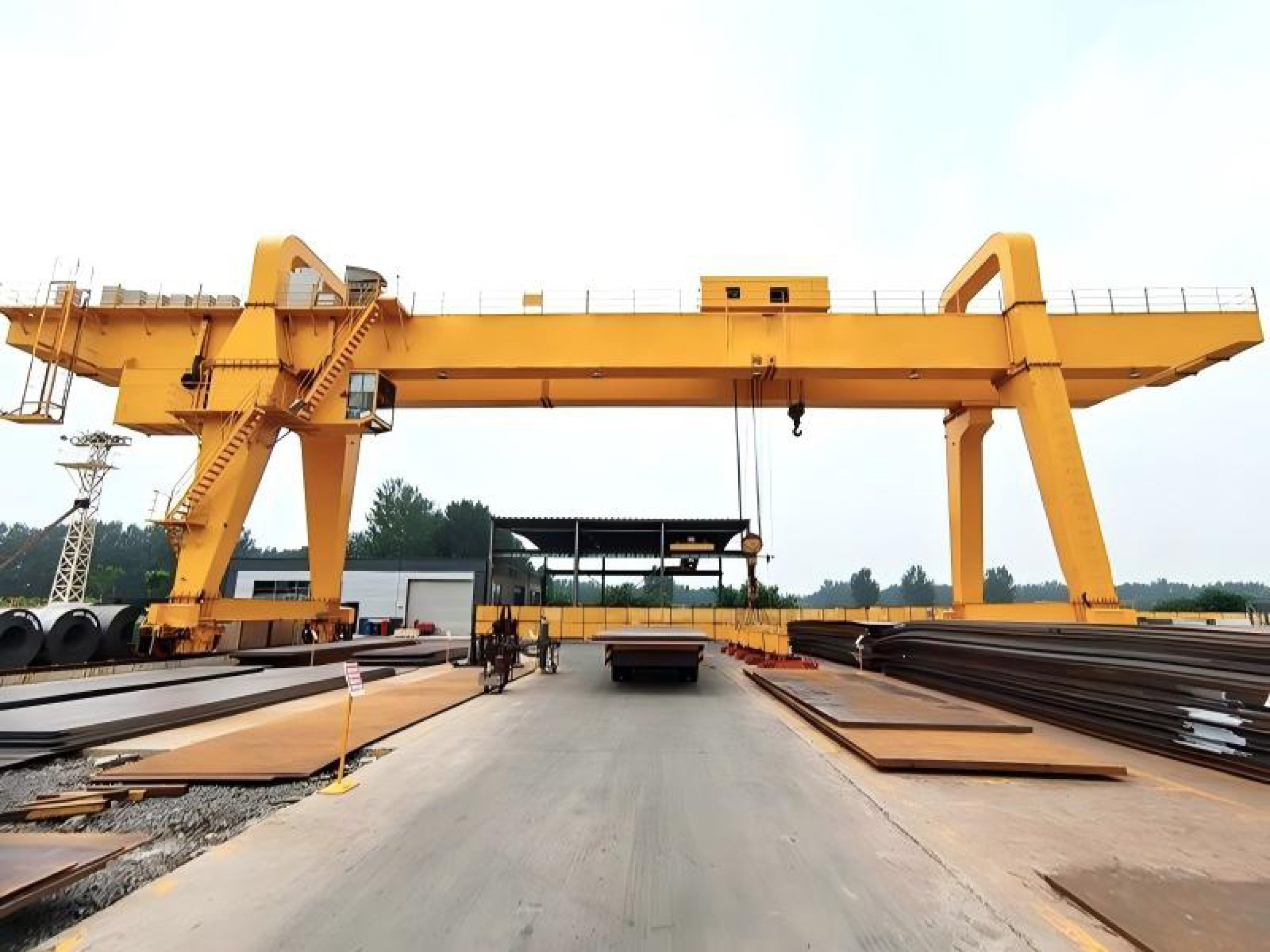

3. Flexible Motion Control for Complex Applications
These cranes are capable of multi-directional movement, including hoisting, lowering, longitudinal travel, cross traverse, and even rotation when equipped with a slewing device. Modern systems often feature anti-sway technology and laser positioning for precise load placement and reduced swing during transport. Such flexibility makes them suitable for complex tasks like assembly operations, workshop logistics, and handling irregularly shaped loads.
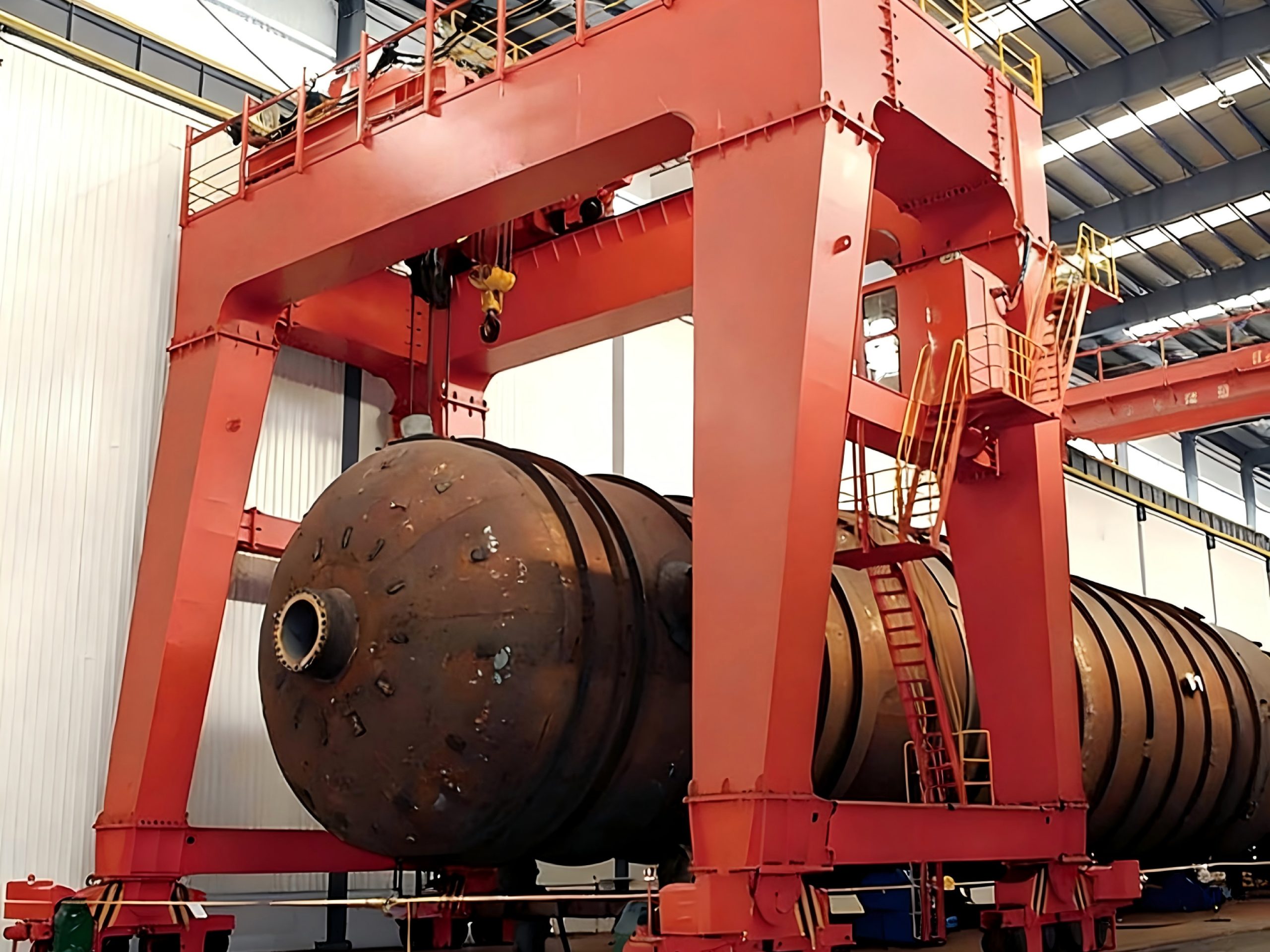

4. Intelligent Control Systems for Safe and Accurate Operation
Contemporary double-girder gantry cranes commonly employ variable frequency drives (VFD) and PLC-based automation, enabling smooth speed control and accurate positioning. They can be operated via remote control or from an ergonomic cabin interface. Safety is reinforced through devices such as overload limiters, height limit switches, travel end buffers, emergency stop functions, and storm-resistant anchoring systems. Advanced models may also include real-time monitoring and self-diagnostic features, minimizing operational risks and ensuring reliable performance during continuous use.
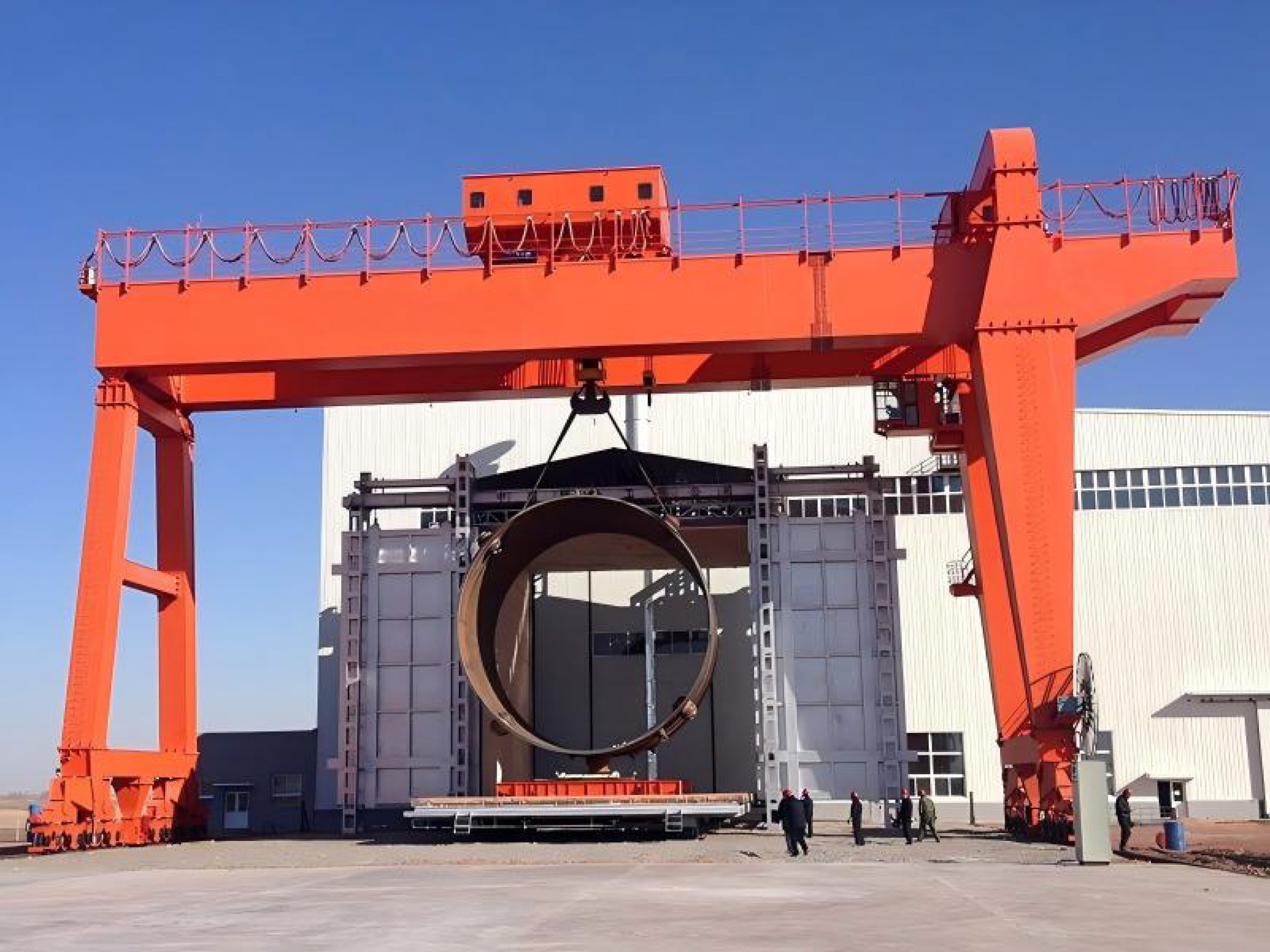

5. Strong Environmental Adaptability and Customization Options
These cranes can be customized to suit various working conditions, including:
1.Corrosion- and dust-resistant designs for chemical or coastal environments;
2.Low- or high-temperature adaptations using specialized steels and lubricants;
3.Explosion-proof configurations for hazardous areas;
4.Versatile track options, including ground rails, suspended rails, or even rubber-tired or crawler-mounted mobile versions.
This high degree of customization allows integration into diverse production and logistics workflows.
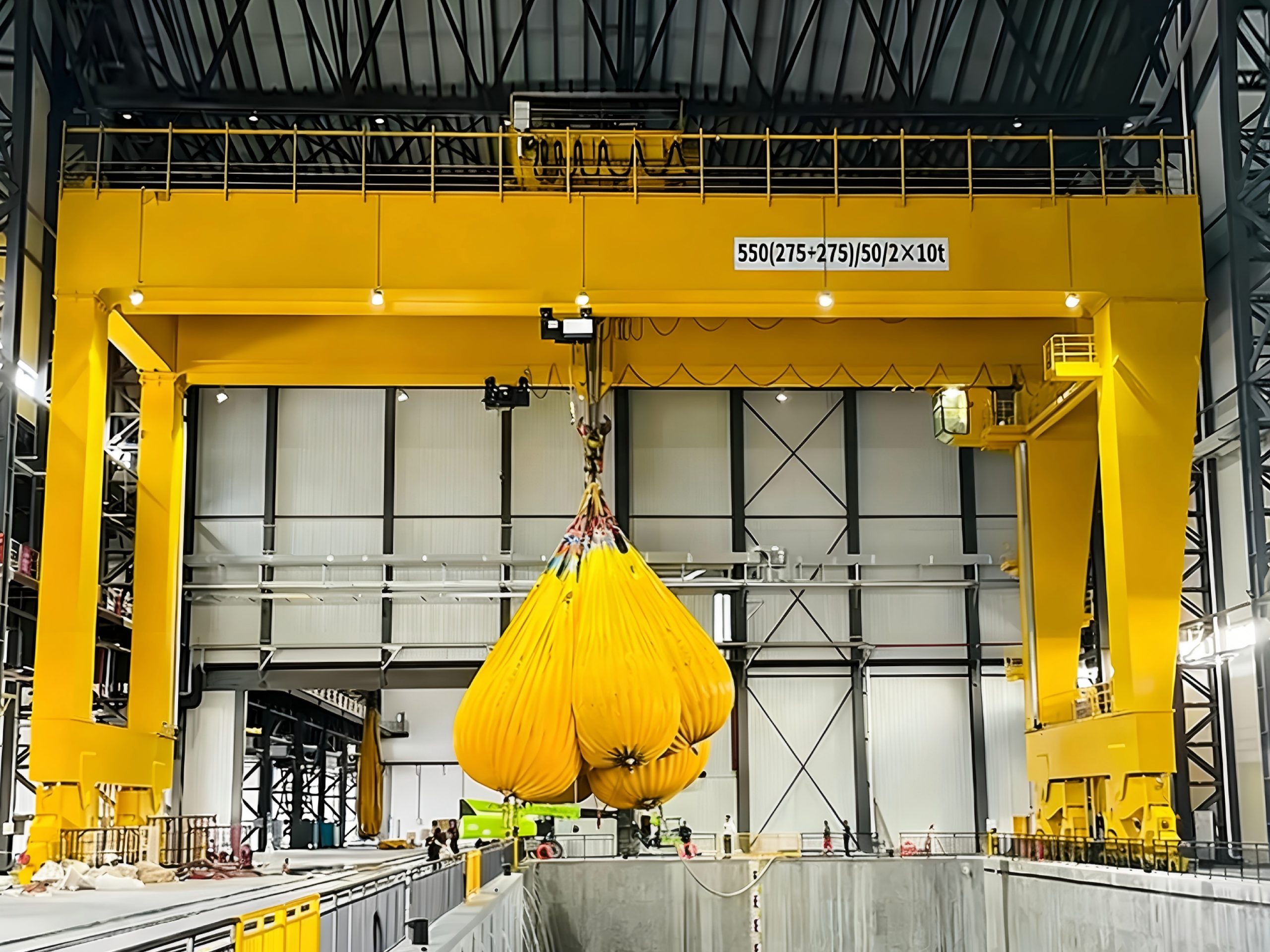

6. Ease of Maintenance and Cost-Effectiveness
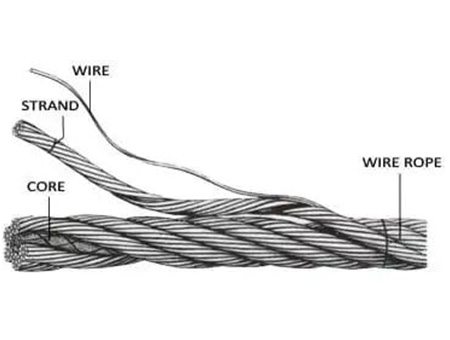
Although the double-girder structure is more complex, key components such as wheel sets, gearboxes, and wire ropes are often modular in design, simplifying inspection, replacement, and maintenance. Many newer cranes are also equipped with centralized lubrication systems and condition-monitoring sensors, facilitating predictive maintenance and reducing unplanned downtime. Over their lifecycle, their high load capacity, reliability, and long service life offer users a strong return on investment.
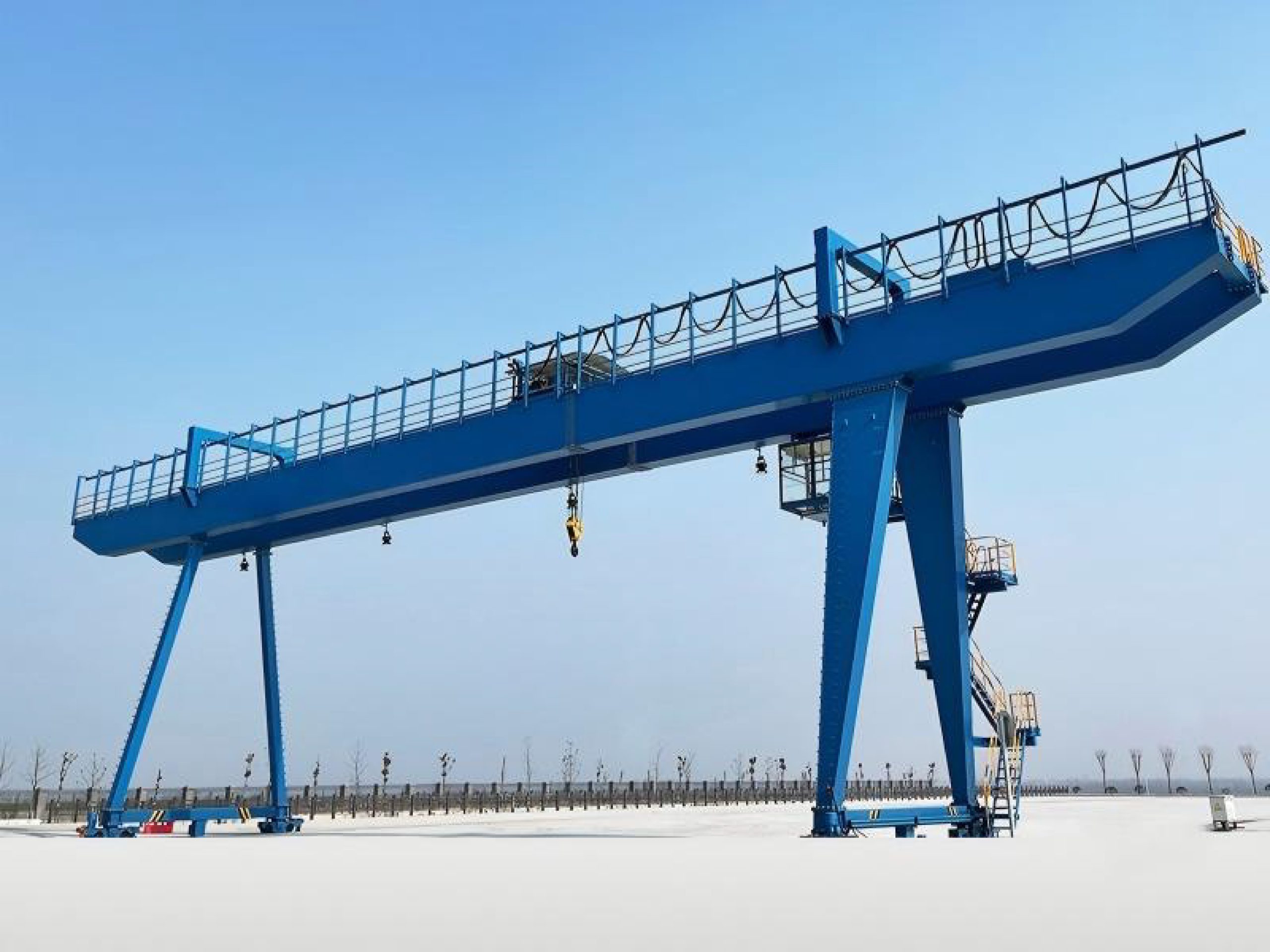

In summary, double-girder gantry cranes stand out due to their structural strength, broad operational coverage, precise and flexible control, advanced safety features, and excellent adaptability. With ongoing integration of smart and sustainable technologies, their role in industrial advancement and large-scale infrastructure projects will continue to grow.