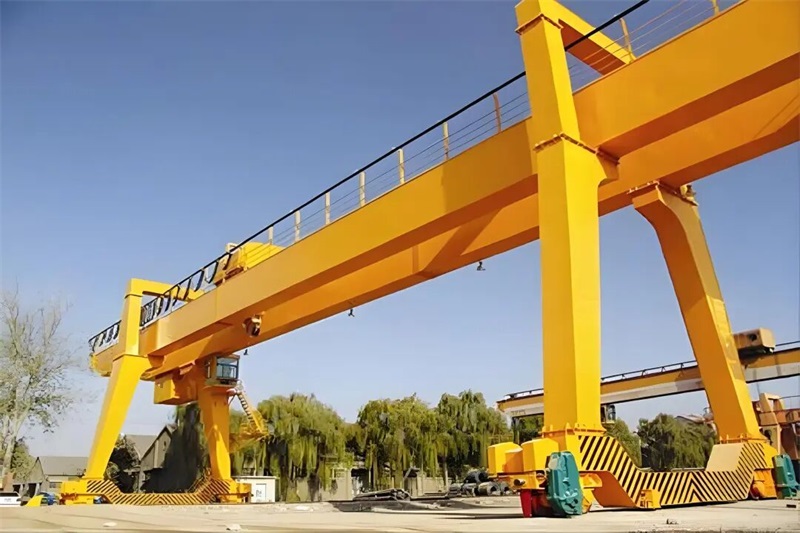
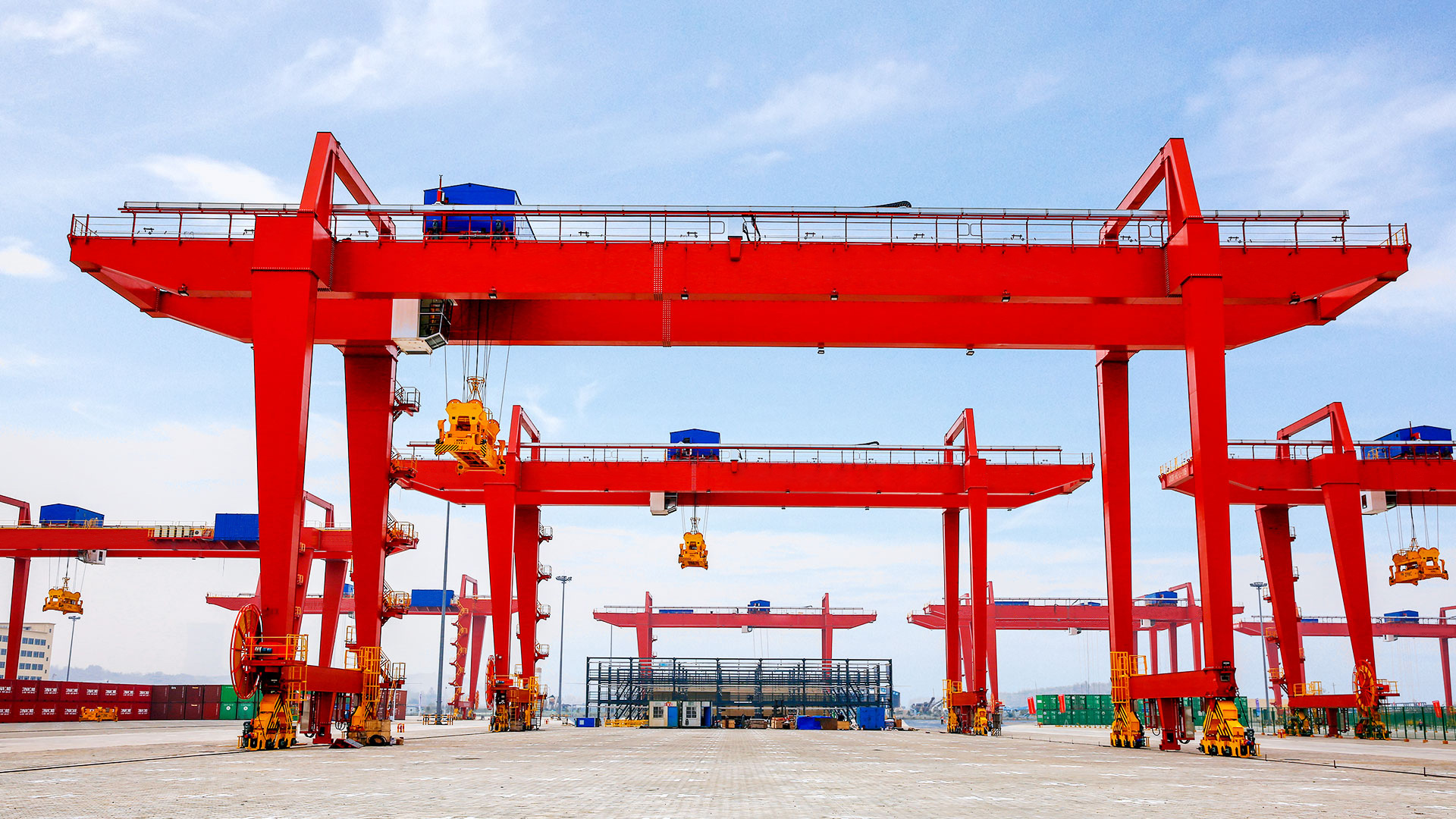
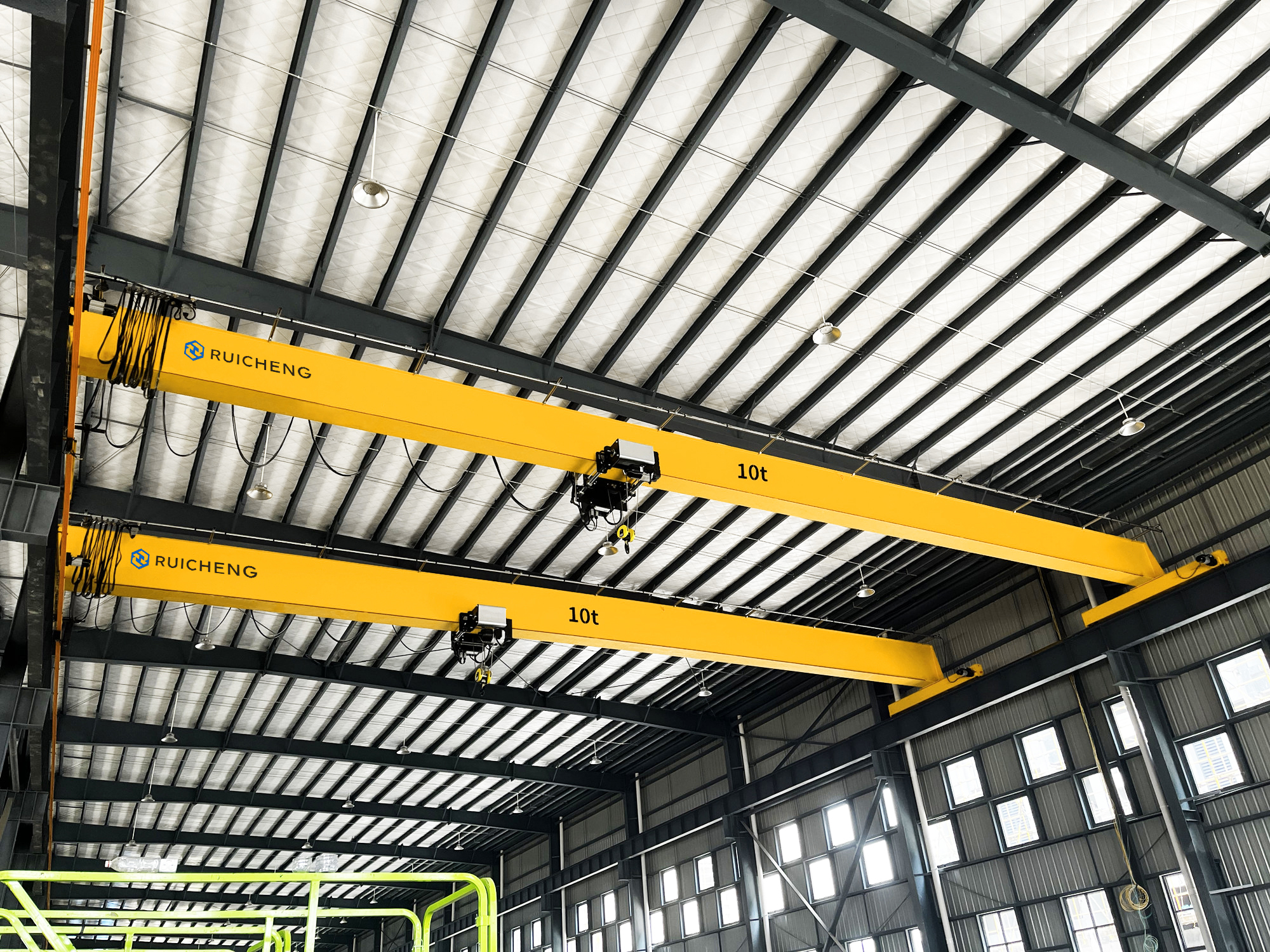
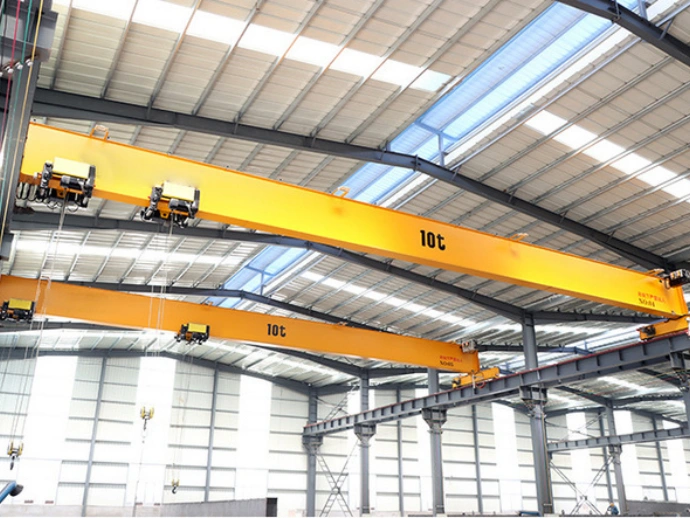
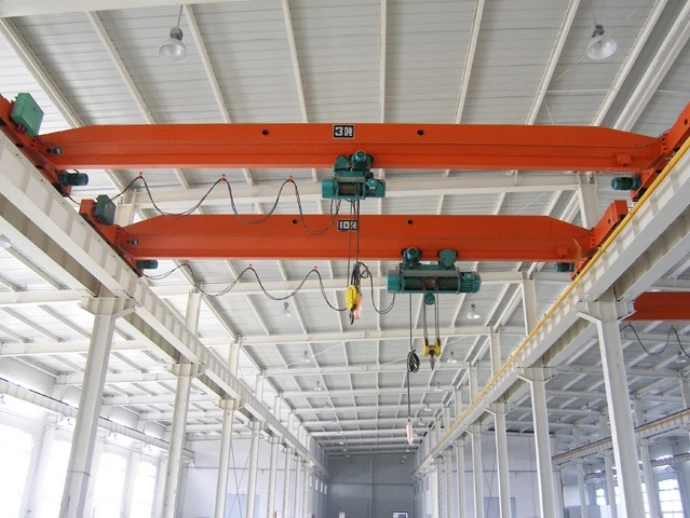
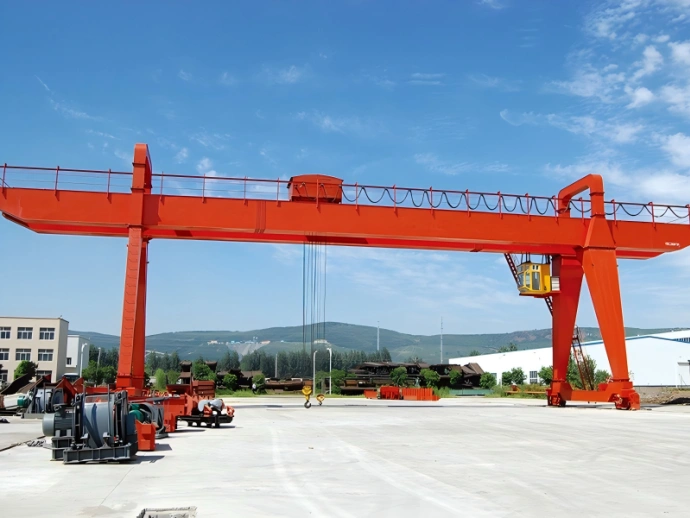
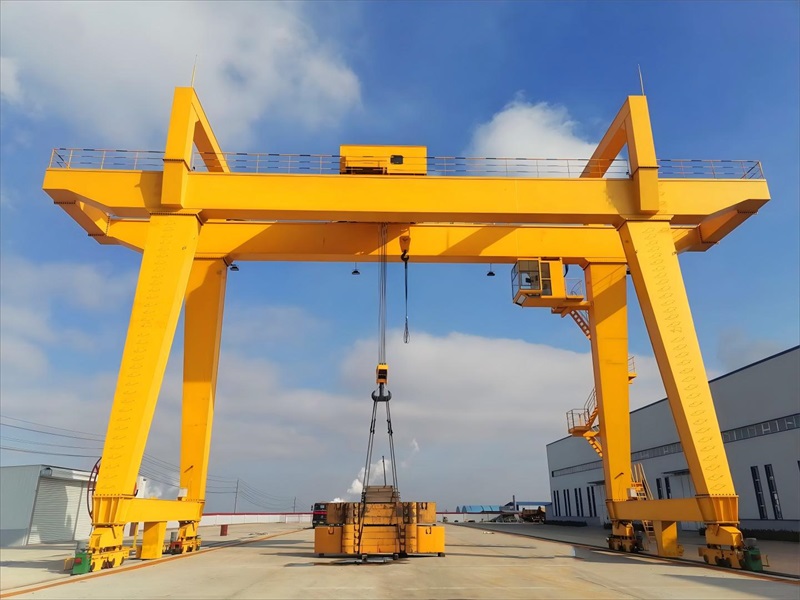
A cantilever gantry crane is a type of gantry or semi-gantry crane whose main girder extends beyond the crane’s runway rails on one or both sides. This design enables the crane to handle materials beyond the standard span, providing greater operational range and flexibility without the need to move the entire crane. Commonly used in ports, storage yards, factories, and other heavy-duty material handling environments requiring extended reach, it should be noted that the cantilever is not a standalone type of crane but rather a structural modification to a standard gantry crane.

Understanding the Role of the Cantilever
The cantilever is a beam structure extending outward from the main girder beyond the crane’s runway rails. Its primary purpose is to expand the crane’s working range without altering the track layout. More specifically:
- Expanding the Working Range:By extending beyond the runway, the crane can cover a broader material handling area and adapt flexibly to confined spaces.
- Improving Operational Efficiency:Reduces unnecessary repositioning, shortens handling time, and significantly enhances overall productivity.
- Providing Broad Applicability:With these advantages, cantilever gantry cranes are highly effective in ports, storage yards, factories, and other industrial environments.
By extending the main girder beyond the runway, the cantilever enables operations both within and outside the span, thereby boosting productivity while minimizing repositioning or downtime.
Key Advantages of Cantilever Gantry Cranes
In addition to the above functions, the cantilever structure offers distinct operational benefits, which can be summarized as follows:
- Lifting and Transporting Goods:The cantilever allows vertical lifting and horizontal movement to reach areas beyond the normal crane span.
- Expanding the Working Range:Even in narrow or restricted spaces, the cantilever can cover a wider material handling area.
- Enhancing Efficiency: With less need for repositioning, operations become faster, and multiple lifts can often be performed within the same span.
Thanks to these advantages, cantilever gantry cranes are particularly suitable for ports, large factories, storage yards, and construction sites. By cleverly extending the crane beyond the tracks, operators can handle oversized or off-track materials without interfering with internal operations.
How to Determine the Appropriate Cantilever Length
After understanding its functions and advantages, the next step is to determine the cantilever length. Selecting the correct length is crucial for both safety and efficiency.
Structural Load and Self-Weight: A longer cantilever increases the crane’s self-weight and the pressure on its supports.
Working Radius: The effective reach depends on the horizontal distance from the load support point to the outer edge of the main girder.
Environmental Factors: Wind loads, extreme temperatures, high-altitude operations, and corrosive environments must be considered.
Operational Conditions: Load frequency, lifting height, hook configuration, and site layout all influence the safe cantilever length.
In practice, typical cantilever lengths range from 6 to 12 meters, balancing reach with structural integrity. In actual projects, professional engineers should always perform calculations for stress, deflection, wheel loads, and stability to verify that the cantilever can operate safely under expected loads.
Cantilever Sizing Design Process
Define the duty group and load spectrum (ISO/FEM/CMAA).
Determine the rated load and calculate load cases, including static, dynamic, wind, and speed-related forces.
Predefine the cantilever envelope dimensions based on hook reach and site clearance requirements.
Perform structural checks: girder stress, deflection limits, wheel loads, and stability margins.
Iterate the process until safety and operational requirements are met.